Physical therapy: Who can benefit and how can it help?
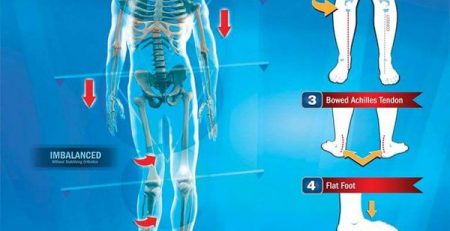
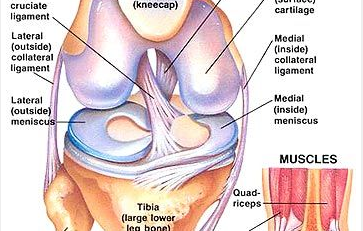
Orthopedic physical therapy treats musculoskeletal injuries, involving the muscles, bones, ligaments, fascias, and tendons. It is suitable for medical conditions such as fractures, sprains, tendonitis, bursitis, chronic medical problems, and rehabilitation or recovery from orthopedic surgery. Patients may undergo treatment with joint mobilizations, manual therapy, strength training, mobility training, and other modalities.
Geriatric physical therapy can help older patients who develop conditions that affect their mobility and physical function, including arthritis, osteoporosis, Alzheimer’s disease, hip and joint replacement, balance disorders, and incontinence. This type of intervention aims to restore mobility, reduce pain and increase physical fitness levels.
Neurological physical therapy can help people with neurological disorders and conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, brain injury, cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, spinal cord injury, and stroke. Treatment may aim to increase limb responsiveness, treat paralysis, and reverse increase muscles strength by reducing muscle atrophy.
Cardiovascular and pulmonary rehabilitation can benefit people affected by some cardiopulmonary conditions and surgical procedures. Treatment can increase physical endurance and stamina.
Pediatric physical therapy aims to diagnose, treat, and manage conditions that affect infants, children, and adolescents, including developmental delays, cerebral palsy, spina bifida, torticollis and other conditions that impact the musculoskeletal system.
Wound care therapy can help to ensure that a healing wound is receiving adequate oxygen and blood by way of improved circulation. Physical therapy may include the use of manual therapies, electric stimulation, compression therapy and wound care.Vestibular therapy aims to treat balance problems that can result from inner ear conditions. Vestibular physical therapy involves a number of exercises and manual techniques that can help patients regain their normal balance and coordination.
Decongestive therapy can help to drain accumulated fluid in patients with lymphedema and other conditions that involve fluid accumulation.
Pelvic floor rehabilitation can help treat urinary or fecal incontinence, urinary urgency and pelvic pain in men and women as a result of injuries or surgery, or because of certain conditions.
Apart from physical manipulation, physical therapy treatment may involve:
- Ultrasound, to promote blood flow and healing by heating the tendons, muscles, and tissues
- Phonophoresis, which uses ultrasound to deliver certain medications such as topical steroids. This can decrease the presence of inflammation
- Electrical stimulation, or E-stim, which uses topical electrodes on the skin to reduce pain and increase functional capabilities. One type of E-stim is transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS). At times, anti-inflammatory medications are used with certain E-stim modalities and is referred to as iontophoresis
- Heat, moist heat and cold therapy
- Light therapy, in which special lights and lasers are used to treat certain medical conditions